A commonly asked question in today's energy and political landscape. Our goal within this blog is to provide you with accurate and up-to-date information so you can assess whether a heat pump is the right source of heat for your heating and cooling needs.
How do heat pumps work?
Air source and ground source heat pumps operate on an efficient principle; they transfer units of heat from one place to another rather than generating heat directly. This process is based on the refrigeration cycle, which involves refrigerant fluid that circulates within the system.
The main components of a modern heat pump include the evaporator, compressor, condenser, and expansion valve. The refrigerant absorbs heat at the evaporator by changing from a liquid to a gas. This gaseous refrigerant is then compressed, which raises its temperature, and is released as heat at the condenser. The expansion valve lowers the pressure of the refrigerant, allowing it to cool down before it re-enters the evaporator to repeat the cycle.
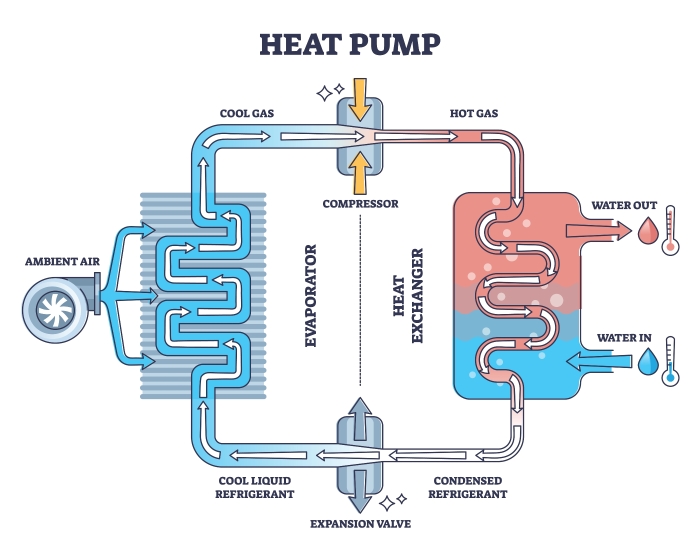
The efficiency of this process allows heat pumps to move more energy than they consume, which is why they are considered an energy-efficient heating and cooling option – which can translate to energy, monetary savings along with reduced carbon emissions.
Understanding how heat pumps work and heat pump system design are crucial when considering whether heat pumps are worth it, especially when comparing against natural gas boilers or traditional boilers.
For design support for hot water, central heating or underfloor heating, contact the Rinnai design support team today.
Types of heat pumps
There are several types of heat pumps available, each designed to meet different environmental conditions and user requirements. The most common types include air-source heat pumps, ground-source or geothermal heat pumps, and water-source heat pumps.
Air-source heat pumps are the most widely used and they are an excellent technology to lower a site's carbon footprint as they extract heat from the outdoor air, making them suitable for a variety of climates. They are relatively easy to install and can be used in both residential and commercial properties. R290 or high temperature heat pump variants are a popular choice as they can achieve water temperatures of over 65 degrees Celsius even in cold weather. This in turn reduces the need for electric boilers or modern gas boilers as a back up.
Ground-source heat pumps, also known as geothermal heat pumps, utilise the stable temperature of the earth to provide heating and cooling. These systems require more extensive installation due to the need for underground piping, but they are highly efficient and can result in lower operating costs over time, however their initial cost is often higher than other heat pump installations. Ground-source systems are particularly advantageous in extreme climates, where air-source systems may struggle to maintain efficiency during very cold temperatures.
Water-source heat pump technology operates by transferring heat to or from a body of water, such as a lake, river, or well. These systems are less common but can be very efficient in areas with suitable water sources. Additionally, there are hybrid heat pumps that combine two different types of systems, allowing for greater flexibility and efficiency. Understanding the various types of heat pumps available is essential, as it helps potential buyers choose the right system that aligns with their specific heating and cooling needs, as well as their budget.
Factors that affect the cost of heat pumps
There are many factors affecting the assessment of whether these renewable sources of heat are worth it.
Firstly, the average cost of the technologies can vary widely based on several key factors. One of the primary determinants is the type of heat pump selected. For instance, air-source heat pumps generally have lower upfront costs compared to ground-source systems, which require significant excavation and installation efforts. Additionally, the size and capacity of the technology needed for a specific space will also impact the overall cost. Larger commercial buildings may require units of electricity, which can drive up both equipment and installation costs.
Another important factor is the installation complexity and whether planning permission is required. The location of the installation site can influence the cost, as installations in densely populated or urban areas may require special permits or additional labor. Furthermore, the expertise of the low carbon heating systems installer can affect pricing, as highly certified and experienced professionals may charge a premium for their services.
Energy efficiency ratings also play a role in determining the cost of heat pumps. Higher-efficiency models may have a higher initial price but can lead to significant savings on energy bills over time due to their lower energy consumption.
Investing in heat pump technology with a good Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio (SEER), coefficient of performance, SCOP or Heating Seasonal Performance Factor (HSPF) rating, will directly affect long-term operating costs.
Ultimately, understanding these factors can help regarding the most suitable heat pump technology for your project needs while balancing upfront costs with long-term savings.
Installation costs
The financial investment in installation costs for heat pumps can vary significantly based on several variables, including the type of heat pump, the complexity of the installation, and the region in which the project is situated.
Additional costs may arise from necessary modifications to your commercial project such as electrical upgrades, or even structural changes to support for instance a large outdoor unit. The supporting ancillaries products can also play a significant role in increasing the project costs, especially in commercial applications.
To understand the capital expenditure, operational expenditure and carbon modelling of traditional heating system when compared to full heat pump or hybrid heat pump and solar panel systems, contact us today through our carbon cost comparison form.
Energy savings and cost benefits
One of the most compelling reasons to consider a heat pump is the potential for significant energy savings and carbon reduction. The efficiency of heat pumps is an important factor as they can often deliver three to four times more heat energy or cooling energy than the electrical energy they consume. This high level of efficiency can lead to lower utility costs and a significant carbon reduction when compared to gas boilers or oil boilers.
Over time, these savings can offset the initial investment in the system, making heat pumps a smart choice, however in commercial properties it is essential to understand how the full system installation operates and runs to manage optimal performance and cost expectations effectively.
Moreover, the environmental benefits of heat pumps should not be overlooked. By using renewable energy sources, such as the heat from air or ground, heat pumps can reduce greenhouse gas emissions compared to traditional fossil fuel heating systems. This contribution to sustainability can be an essential consideration for eco-conscious consumers looking to minimise their environmental impact while enjoying long-term savings on energy costs.
For more information about understanding the SPF (Season Performance Factors) of heat pumps including how SPF can lead to financial savings, book on to a free CPD course today.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the cost of different HP technology is vital when considering this popular choice for heating and hot water projects. By exploring how heat pumps work, the technology available, factors influencing their costs such as space, additional remedial works, ancillary product requirements, including for larger radiators, SPF and energy costs, the system performance can be effectively compared meaning that building operators, consultants and estates managers can make informed decisions that align with their budgets and needs from a practical, economic and technical performance perspective.
Installation and maintenance costs, as well as financing options like the boiler upgrade scheme and electricity prices play crucial roles in determining the overall financial implications of owning and operating a heat pump.
Investing in a heat pump may require a higher initial outlay compared to traditional heating systems, but the long-term savings on energy bills, combined with the ESG requirements to achieve climate targets, can make them a worthwhile investment.
Ultimately, the decision to install a heat pump should be based on careful planning, cost analysis, and consideration of individual preferences and circumstances. With the right information and planning, estates managers and building operators can reap the financial and environmental benefits that heat pumps have to offer.
For support on the key consideration above, contact Rinnai today.
Updated April 2025
Last updated Jan 2025

